AI and Scientific Development: A New Era of Materials
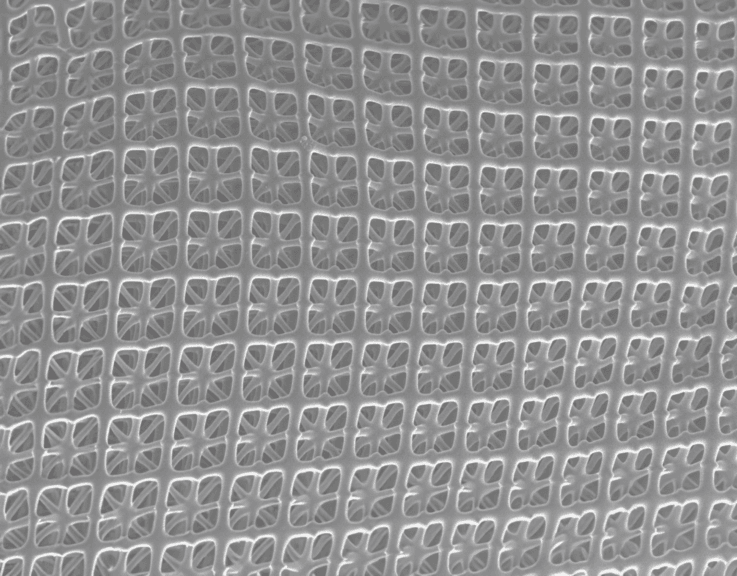
Nanoarchitectonic material
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and scientific development is ushering in a new era of materials science. A recent breakthrough has yielded a nanoarchitectonic material that promises to redefine the boundaries of engineering, particularly in aerospace. This material, combining the strength of carbon steel with the lightness of polystyrene foam, is not just a concept; it's a reality, and it's poised to change space travel forever.
Key Points:
Unprecedented Material Characteristics:
This novel material boasts a strength five times greater than titanium while maintaining the lightweight properties of polystyrene foam.
It can withstand a stress of 2.03 megapascals per cubic meter per kilogram of its density, a remarkable feat in material science.
AI-Driven Development Process:
Machine learning played a pivotal role in designing the optimal geometric structure, showcasing the power of AI in materials research.
A multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm was employed, requiring only 400 data points, significantly less than the 20,000+ needed by traditional methods.
Two-photon polymerization 3D printing was used to create intricate micro and nano-scale prototypes.
These structures were then subjected to high-temperature treatment (900°C) to yield high-purity sp² carbon.
Structure and Composition:
The material is composed of carbon nanolattices with an ultrafine lattice structure, demonstrating advanced nanotechnology.
The lattice pillars have a diameter of just 300 nanometers, highlighting the precision of the manufacturing process.
The design removes sharp corners in the lattice, greatly reducing stress points.
Potential Applications Across Industries:
Aerospace: Enables the creation of ultralight parts for airplanes, helicopters, and spacecraft, revolutionizing space exploration.
Automotive: Contributes to significant weight reduction in vehicles, leading to increased fuel efficiency.
Significant fuel savings are possible, estimations show around 80 liters of fuel saved per kilogram of replaced material per year in aircraft.
Transformative Impact:
Substantial reduction in aircraft weight, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions, addressing critical environmental concerns.
Facilitates the construction of larger components in orbit, overcoming the limitations of current rocket payload capacities.
Opens the possibility of in-situ resource utilization for construction on the Moon or Mars, using locally sourced materials.
This technological leap exemplifies the synergy between AI, nanotechnology, and additive manufacturing, paving the way for materials with unparalleled properties.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
Q: How does AI contribute to the development of this material?
A: AI, particularly machine learning algorithms, is used to optimize the material's geometric structure, significantly reducing the number of experimental data points needed.
Q: What makes this material stronger than titanium?
A: The unique nanoarchitectonic structure and the use of high-purity sp² carbon, combined with a design that eliminates stress points, contribute to its exceptional strength.
Q: What are the primary applications of this material?
A: Primarily in aerospace for creating ultralight components, and in the automotive industry for weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency.
Q: Can this material be used for construction on other planets?
A: Yes, its properties make it suitable for constructing structures on the Moon or Mars, potentially using locally available materials.
Q: How is this material produced?
A: It is produced using two-photon polymerization 3D printing to create nano-scale structures, followed by high-temperature treatment to form high-purity carbon.