A Revolutionary Miniature Swimming Robot Inspired by Nature
Miniature Swimming Robot
Cutting-Edge Aquatic Exploration
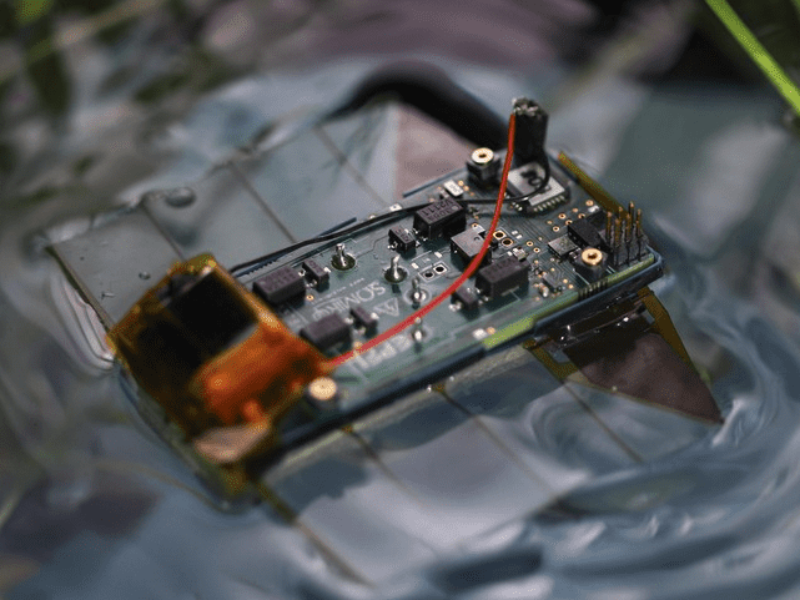
Scientists have made a breakthrough in aquatic exploration with the development of an innovative miniature swimming robot inspired by marine flatworms. This tiny device, smaller than a credit card and weighing only six grams, has the potential to revolutionize environmental monitoring and the study of aquatic ecosystems.
Bio-Inspired Design
Created by researchers from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, the robot utilizes a silent propulsion system based on undulating fins, mimicking the movement of marine flatworms. This feature enables it to:
Navigate seamlessly through turbulent water surfaces.
Reach speeds of up to 12 centimeters per second.
Maneuver efficiently in confined spaces.
Technical Features
Innovative Propulsion: The robot employs four artificial muscles to power its fins, granting it unprecedented maneuverability, including the ability to swim backward and laterally.
Advanced Control System: A compact electronic system supplies up to 500 volts to the robot’s actuators while consuming only 500 milliwatts of power.
Intelligent Sensors: Equipped with light sensors functioning as rudimentary eyes, the robot autonomously follows light sources.
Potential Applications
This miniature swimming robot has a wide range of potential applications, including:
Mapping pollution levels in water bodies.
Studying sensitive aquatic ecosystems like coral reefs.
Monitoring water quality in lakes and rivers.
Conducting inspections in confined aquatic spaces, such as rice fields.
Advantages Over Traditional Systems
Unlike conventional aquatic robots that rely on noisy propellers, this new design offers several key advantages:
Silent Operation: Does not disturb wildlife.
Seamless Environmental Integration: Blends naturally into aquatic settings.
Superior Energy Efficiency: Consumes minimal power while maintaining effective performance.
Future Prospects
Researchers aim to further enhance this promising robotic system by:
Extending operational runtime.
Improving autonomy.
Developing a more robust platform for field testing.
Dr. Florian Hartmann, head of the research group, states: "Our design does not merely replicate nature; it surpasses what natural organisms can achieve." This advancement not only propels bio-inspired robotics forward but also lays the foundation for practical robotic systems that harmonize with nature.
Conclusion
This tiny swimming robot represents a significant leap in environmental monitoring technology, unlocking new possibilities for ecological research and the protection of fragile aquatic ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How does this robot differ from traditional aquatic robots?
Unlike traditional robots with noisy propellers, this design uses silent undulating fins, making it more efficient and less disruptive to marine life.
2. What are the primary applications of this robot?
It can be used for pollution mapping, studying aquatic ecosystems, monitoring water quality, and inspecting confined water environments.
3. How is the robot powered?
It uses a compact electronic system that supplies up to 500 volts to its actuators, consuming only 500 milliwatts of power.
4. What makes this robot more efficient than existing models?
Its bio-inspired propulsion system allows for precise movements, energy efficiency, and the ability to maneuver in confined spaces without disturbing wildlife.
5. What are the future developments planned for this technology?
Researchers aim to enhance autonomy, extend operational durations, and refine the robot's design for practical field applications.